
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY & SPORTS INJURIES
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical technique that can diagnose and treat problems in the knee joint. During the procedure, your surgeon will make a very small incision and insert a tiny camera — called an arthroscope — into your knee. This allows them to view the inside of the joint on a screen. The surgeon can then investigate a problem with the knee and, if necessary, correct the issue using small instruments within the arthroscope.
Arthroscopy diagnoses several knee problems, such as a torn meniscus or a misaligned patella (kneecap). It can also repair the ligaments of the joint. There are limited risks to the procedure and the outlook is good for most patients. Your recovery time and prognosis will depend on the severity of the knee problem and the complexity of the required procedure.
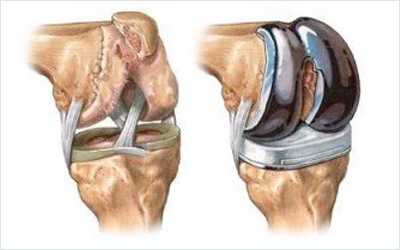
KNEE REPLACEMENT
Once you are under general anesthesia (meaning you are temporarily put to sleep) or spinal/epidural anesthesia (numb below the waist), an 8- to 12-inch cut is made in the front of the knee. The damaged part of the joint is removed from the surface of the bones, and the surfaces are then shaped to hold a metal or plastic artificial joint. The artificial joint is attached to the thigh bone, shin and knee cap either with cement or a special material. When fit together, the attached artificial parts form the joint, relying on the surrounding muscles and ligaments for support and function.

KNEE PRESERVATION
In osteoarthritis of the knee, degeneration of the articular cartilage results in deterioration of the joint surfaces. This results in deformities of both the bones (femur and tibia) and the joint soft tissues, leading to pain, joint stiffness, decreased ROM, gait abnormalities, and malalignment.